On this page you will find a glossary of the main mathematical symbols,
cataloged among the main branches of mathematics in which they are most widely used.
Indeed you will use some of these symbols in order to write in the math-language.
Below you will find a list of the illustrated symbol categories.
Symbols
Greek and Hebrew Letters
These letters are often used in mathematics for variables, constants and unknowns.
| Name | Symbol | Command |
|---|---|---|
| alpha | α | \alpha |
| beta | β | \beta |
| chi | χ | \chi |
| delta | δ | \delta |
| epsilon | ε | \epsilon |
| eta | η | \eta |
| gamma | γ | \gamma |
| iota | ι | \iota |
| kappa | κ | \kappa |
| lambda | λ | \lambda |
| mu | μ | \mu |
| nu | ν | \nu |
| o | o | o |
| omega | ω | \omega |
| phi | φ | \phi |
| pi | π | \pi |
| psi | ψ | \psi |
| rho | ρ | \rho |
| sigma | σ | \sigma |
| tau | τ | \tau |
| theta | θ | \theta |
| upsilon | υ | \upsilon |
| xi | ξ | \xi |
| zeta | ζ | \zeta |
| digamma | ϝ | \digamma |
| varepsilon | ϵ | \varepsilon |
| varkappa | ϰ | \varkappa |
| varphi | ϕ | \varphi |
| varpi | ϖ | \varpi |
| varrho | ϱ | \varrho |
| varsigma | ς | \varsigma |
| vartheta | ϑ | \vartheta |
| Delta | Δ | \Delta |
| Gamma | Γ | \Gamma |
| Lambda | Λ | \Lambda |
| Omega | Ω | \Omega |
| Phi | Φ | \Phi |
| Pi | Π | \Pi |
| Psi | Ψ | \Psi |
| Sigma | Σ | \Sigma |
| Theta | Θ | \Theta |
| Upsilon | Υ | \Upsilon |
| Xi | Ξ | \Xi |
| aleph | ℵ | \aleph |
| beth | ℶ | \beth |
| daleth | ℸ | \daleth |
| gimel | ℷ | \gimel |
CODE
$$\iota \alpha \tau \varepsilon \chi$$
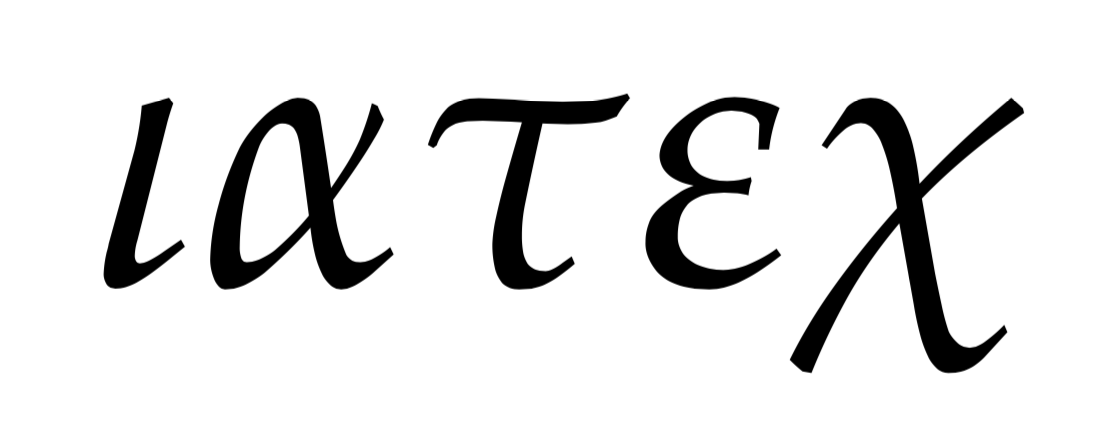
Number Sets
Mathematical sets are essential when we have to define to which of these a number belongs,
in order to exploit certain properties or carry out certain operations.
| Name | Symbol | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Prime | P | \mathbb{P} |
| Whole | W | \mathbb{W} |
| Natural | N | \mathbb{N} |
| Integers | Z | \mathbb{Z} |
| Irrational | I | \mathbb{I} |
| Rational | Q | \mathbb{Q} |
| Real | R | \mathbb{R} |
| Complex | C | \mathbb{C} |
CODE
$$\mathbb{Z}\in\mathbb{R}\notin\mathbb{N}$$

Brackets
When we are faced with numerical expressions of certain dimensions it is essential
to maintain an order, so it is important to define different types of brackets, each of which
indicates a certain priority of calculation.
| Name | Symbol | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Round Brackets | ( ... ) | \left( ... \right) |
| Square Brackets | [ ... ] | \left[ ... \right] |
| Braces | { ... } | \left{ ... \right} |
| Angle Brackets | ⟨ ... ⟩ | \langle ... \rangle |
CODE
$$\left \{ 2 \left [ 6 \left ( 5+1 \right )\right ] \right \} = 72$$
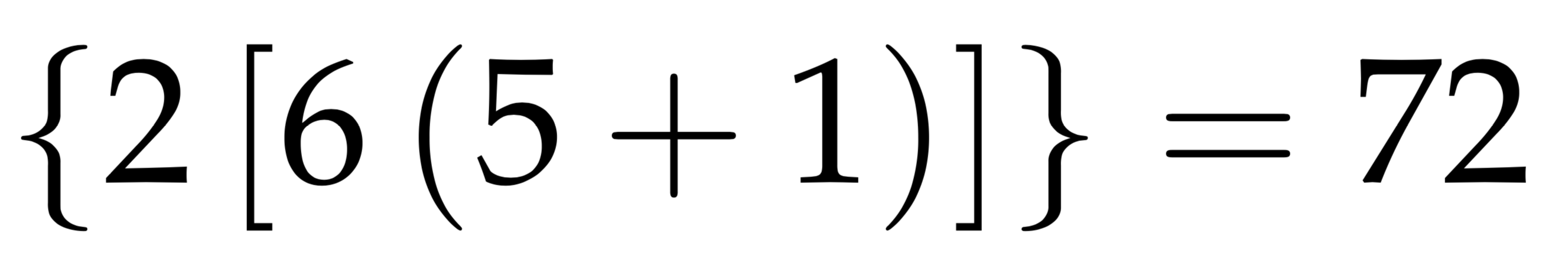
Principal Relation Symbols
These symbols allow us to show characteristics of certain elements.
| Name | Symbol | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Equivalent | ≡ | \equiv |
| Congruent | ≅ | \cong |
| Equal | = | \= |
| Not equal | ≠ | \neq |
| Less or equal | ≤ | \leq |
| Greater or equal | ≥ | \geq |
| Such that | | | \mid |
| Subset | ⊂ | \subset |
| Superset | ⊃ | \supset |
| Element of | ∈ | \in |
| Not element of | ∉ | \notin |
CODE
$$0 \leq 10 > 5 = 5 \neq 2.5 \notin \mathbb{R}$$
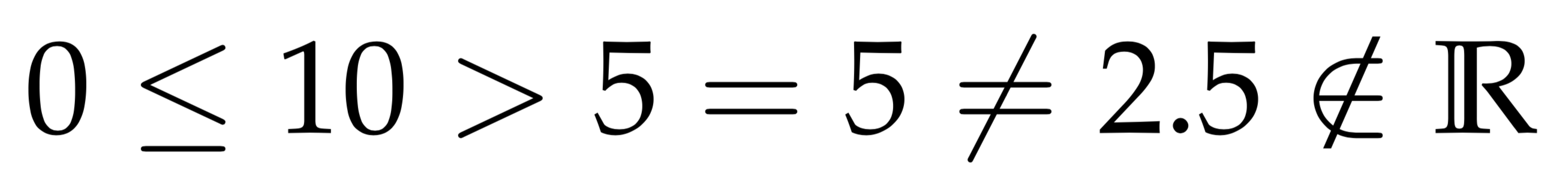
Principal Arrow Symbols
In mathematics the arrows have different uses, one of these is for example
that of showing the equivalence between two equations.
| Name | Symbol | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Left arrow | ← | \leftarrow |
| Right arrow | → | \rightarrow |
| Left-right arrow | ↔ | \leftrightarrow |
| Left double arrow | ⇐ | \Leftarrow |
| Right double arrow | ⇒ | \Rightarrow |
| Left-right big arrow | ⇔ | \geq |
| Left long arrow | ⟵ | \longleftarrow |
| Right long arrow | ⟶ | \longrightarrow |
| Left-right long arrow | ⟷ | \longleftrightarrow |
| Left long double arrow | ⟸ | \Longleftarrow |
| Right long double arrow | ⟹ | \Longrightarrow |
| Left-right long double arrow | ⟺ | \Longleftrightarrow |
| Right arrow from bar | ↦ | \mapsto |
| Right long arrow from bar | ⟼ | \longmapsto |
CODE
$$5 + \alpha = 3 \Leftrightarrow \alpha = 3 - 5 \Leftrightarrow \alpha = -2\\
\rightarrow \alpha = -5$$
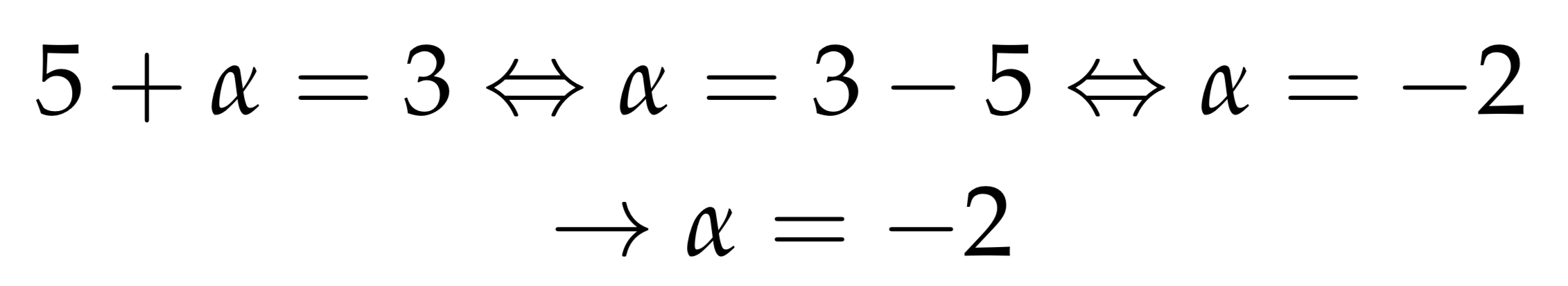
Miscellaneous Symbols
These are some symbols not belonging to the other categories, very often used in mathematics.
| Name | Symbol | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Infinity | ∞ | \infty |
| Plus-minus | ± | \pm |
| Percentage | % | \% |
| Ellipsis | . . . | \cdots |
| Vertical ellipsis | ⋮ | \vdots |
| Oblique ellipsis | - | \ddots |
CODE
$$\infty\pm10\%\infty=\infty$$
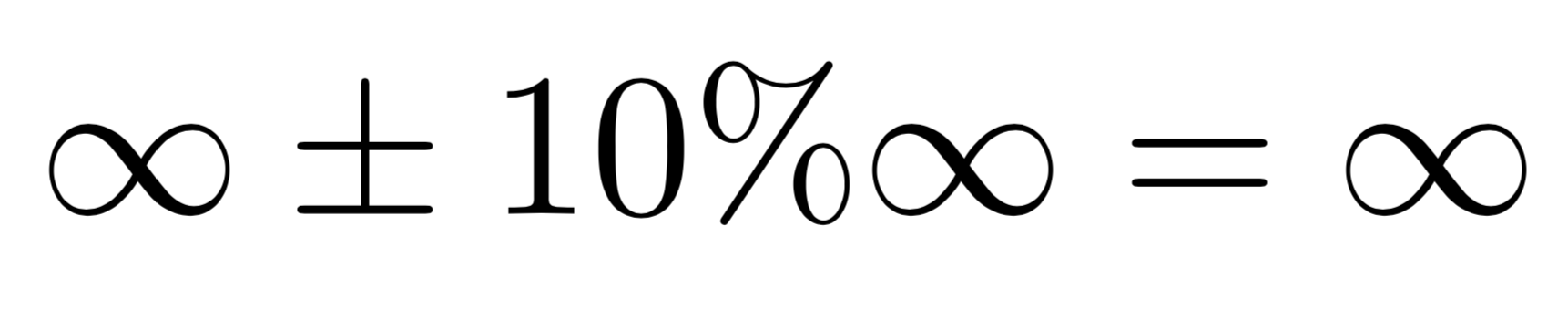
Exercices
1) Write down the code necessary to describe a number set in N which contains α, χ and δ. The set doesn't belong to R. In a second line specify that α > δ and α ≤ χ.
$$\left \{ \alpha;\chi;\delta \right \} \in \mathbb{N} \notin \mathbb{R}$$
$$\alpha>\delta\\, \alpha\leq\chi$$
2) Use one of the two given right arrow from bar in order to built a function which, from two output γ and ω, returns a prime number P.
$$\left ( \gamma, \omega \right ) \mapsto f\left ( \gamma, \omega \right ) \in \mathbb{P}$$
